1.Lua脚本基础语法
Lua是一个简洁、轻量、可扩展的脚本语言
Nginx+Lua优势
充分的结合Nginx的并发处理epool优势和Lua的轻量实现简单的功能且高并发的场景
统计IP
统计用户信息
安全WAF
1.安装lua
[root@Nginx-Lua ~]# yum install lua -y2.lua的运行方式
//命令行执行, 交互式
[root@Nginx-Lua ~]# lua
Lua 5.1.4 Copyright (C) 1994-2008 Lua.org, PUC-Rio
> print("Hello,World")
Hello,World
//文件执行方式, 非交互式
[root@Nginx-Lua ~]# cat test.lua
#!/usr/bin/lua
print("Hi is Bgx!")
[root@Nginx-Lua ~]# lua ./test.lua
Hi is Bgx!3.Lua的注释语法
// --行注释
#!/usr/bin/lua
--print("Hi is Bgx!")
//块注释
--[[
注释代码
--]]4.Lua的基础语法
变量定义
a = 123
//布尔类型只有mil和false
//数字0,空字符串都是true
//lua中的变量如果没有特殊说明, 全是全局变量
while循环语句
[root@nginx ~]# cat while.lua
#!/usr/bin/lua
sum =0
num =1
while num <= 100 do
sum = sum + num
num = num + 1
end
print("sum=",sum)
//执行结果
[root@nginx ~]# lua while.lua
sum= 5050
//Lua没有++或是+=这样的操作for循环语句
[root@nginx ~]# cat for.lua
#!/usr/bin/lua
sum = 0
for i = 1,100 do
sum = sum + 1
end
print("sum=", sum)
//执行结果
[root@nginx ~]# lua for.lua
sum= 100if判断语句
[root@nginx ~]# cat if.lua
#!/usr/bin/lua
if age == 40 and sex == "Man" then
print("男人大于40")
elseif age > 60 and sex ~= "Woman" then
print("非女人而且大于60")
else
local age = io.read()
print("Your age is",age)
end
//~=是不等于
//字符串的拼接操作符".."
//io库的分别从stdin和stdout读写,read和write函数2.Nginx加载Lua环境
默认情况下Nginx不支持Lua模块, 需要安装LuaJIT解释器, 并且需要重新编译Nginx, 建议使用openrestry
LuaJIT
Ngx_devel_kit和lua-nginx-module
1.环境准备
[root@nginx ~]# yum -y install gcc gcc-c++ make pcre-devel zlib-devel openssl-devel2.下载最新的luajit和ngx_devel_kit以及lua-nginx-module
[root@nginx ~]# mkdir -p /soft/src && cd /soft/src
[root@nginx ~]# wget http://luajit.org/download/LuaJIT-2.0.4.tar.gz
[root@nginx ~]# wget https://github.com/simpl/ngx_devel_kit/archive/v0.2.19.tar.gz
[root@nginx ~]# wget https://github.com/openresty/lua-nginx-module/archive/v0.10.13.tar.gz3.解压ngx_devel_kit和lua-nginx-module
//解压后为ngx_devel_kit-0.2.19
[root@nginx ~]# tar xf v0.2.19.tar.gz
//解压后为lua-nginx-module-0.9.16
[root@nginx ~]# tar xf v0.10.13.tar.gz4.安装LuaJIT Luajit是Lua即时编译器。
[root@nginx ~]# tar zxvf LuaJIT-2.0.3.tar.gz
[root@nginx ~]# cd LuaJIT-2.0.3
[root@nginx ~]# make && make install5.安装Nginx并加载模块
[root@nginx ~]# cd /soft/src
[root@nginx ~]# wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.12.2.tar.gz
[root@nginx ~]# tar xf nginx-1.12.2.tar.gz
[root@nginx ~]# cd nginx-1.12.2
./configure --prefix=/etc/nginx --with-http_ssl_module \
--with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_dav_module \
--add-module=../ngx_devel_kit-0.2.19/ \
--add-module=../lua-nginx-module-0.10.13
[root@nginx ~]# make -j2 && make install
//建立软链接, 不建立会出现share object错误
ln -s /usr/local/lib/libluajit-5.1.so.2 /lib64/libluajit-5.1.so.2
//4.加载lua库,加入到ld.so.conf文件
echo "/usr/local/LuaJIT/lib" >> /etc/ld.so.conf
ldconfig也可以直接部署春哥的开源项目OpenResty
//安装依赖包
# yum install -y readline-devel pcre-devel openssl-devel
# cd /soft/src
下载并编译安装openresty
# wget https://openresty.org/download/ngx_openresty-1.9.3.2.tar.gz
# tar zxf ngx_openresty-1.9.3.2.tar.gz
# cd ngx_openresty-1.9.3.2
# ./configure --prefix=/soft/openresty-1.9.3.2 \
--with-luajit --with-http_stub_status_module \
--with-pcre --with-pcre-jit
# gmake && gmake install
# ln -s /soft/openresty-1.9.3.2/ /soft/openresty
//测试openresty安装
# vim /soft/openresty/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
server {
location /hello {
default_type text/html;
content_by_lua_block {
ngx.say("HelloWorld")
}
}
}3.Nginx调用Lua指令
Nginx调用Lua模块指令, Nginx的可插拔模块加载执行, 共11个处理阶段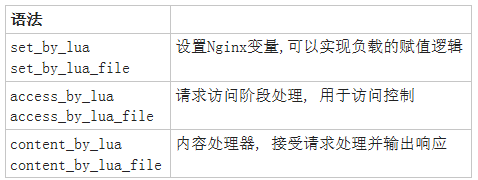
Nginx调用Lua API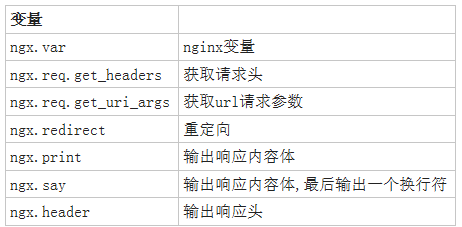
4.Nginx+Lua实现代码灰度发布
使用Nginx结合lua实现代码灰度发布
按照一定的关系区别,分不分的代码进行上线,使代码的发布能平滑过渡上线
1.用户的信息cookie等信息区别
2.根据用户的ip地址, 颗粒度更广
实践架构图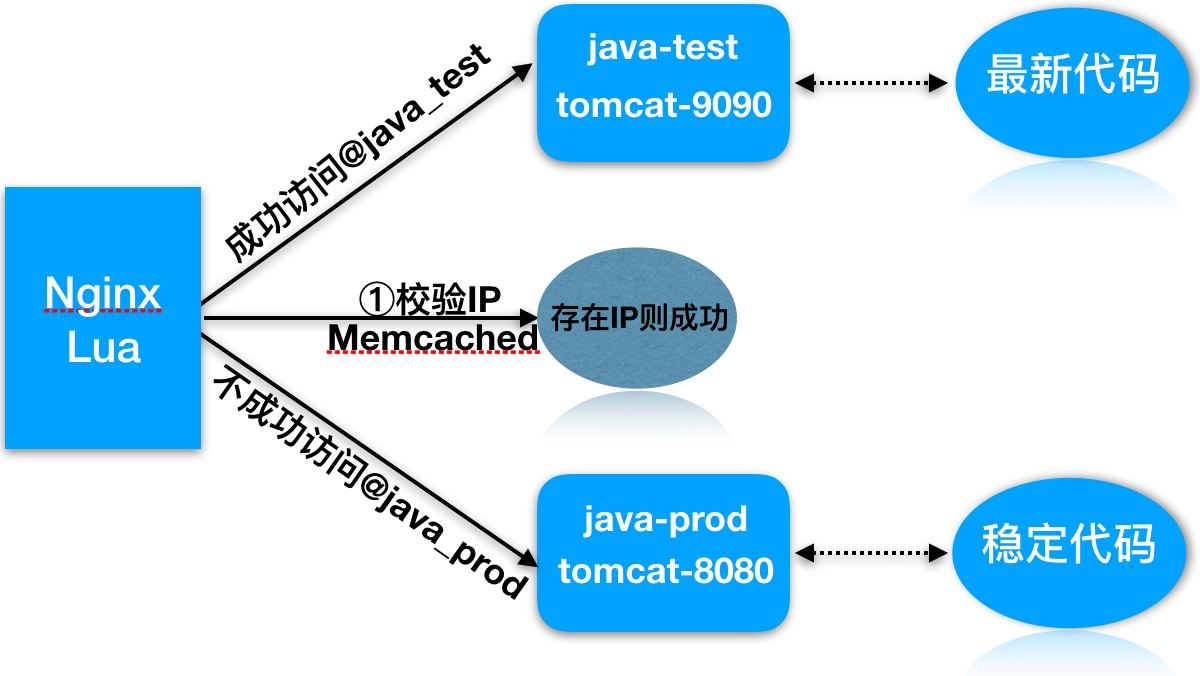
执行过程:
1.用户请求到达前端代理Nginx, 内嵌的lua模块会解析Nginx配置文件中Lua脚本
2.Lua脚本会获取客户端IP地址,查看Memcached缓存中是否存在该键值
3.如果存在则执行@java_test,否则执行@java_prod
4.如果是@java_test, 那么location会将请求转发至新版代码的集群组
5.如果是@java_prod, 那么location会将请求转发至原始版代码集群组
6.最后整个过程执行后结束
实践环境准备: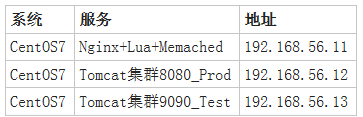
1.安装两台服务器Tomcat,分别启动8080和9090端口
[root@tomcat-node1-20 ~]# yum install java -y
[root@tomcat-node1-20 ~]# mkdir /soft/src -p
[root@tomcat-node1-20 ~]# cd /soft/src
[root@nginx ~]# wget http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/apache/tomcat/tomcat-9/v9.0.7/bin/apache-tomcat-9.0.7.tar.gz
[root@tomcat-node1-20 src]# tar xf apache-tomcat-9.0.7.tar.gz -C /soft
[root@tomcat-node1-20 soft]# cp -r apache-tomcat-9.0.7/ tomcat-8080
[root@tomcat-node1-20 bin]# /soft/tomcat-8080/bin/startup.sh
//注意tomcat默认监听在8080端口, 如果需要启动9090端口需要修改server.xml配置文件2.配置Memcached并让其支持Lua调用
//安装memcached服务
[root@Nginx-Lua ~]# yum install memcached -y
//配置memcached支持lua
[root@Nginx-Lua ~]# cd /soft/src
[root@Nginx-Lua ~]# wget https://github.com/agentzh/lua-resty-memcached/archive/v0.11.tar.gz
[root@Nginx-Lua ~]# tar xf v0.11.tar.gz
[root@Nginx-Lua ~]# cp -r lua-resty-memcached-0.11/lib/resty/memcached.lua /etc/nginx/lua/
//启动memcached
[root@Nginx-Lua ~]# systemctl start memcached
[root@Nginx-Lua ~]# systemctl enable memcached3.配置负载均衡调度
#必须在http层
lua_package_path "/etc/nginx/lua/memcached.lua";
upstream java_prod {
server 192.168.56.12:8080;
}
upstream java_test {
server 192.168.56.13:9090;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name 47.104.250.169;
location /hello {
default_type 'text/plain';
content_by_lua 'ngx.say("hello ,lua scripts")';
}
location /myip {
default_type 'text/plain';
content_by_lua '
clientIP = ngx.req.get_headers()["x_forwarded_for"]
ngx.say("Forwarded_IP:",clientIP)
if clientIP == nli then
clientIP = ngx.var.remote_addr
ngx.say("Remote_IP:",clientIP)
end
';
}
location / {
default_type 'text/plain';
content_by_lua_file /etc/nginx/lua/dep.lua;
}
location @java_prod {
proxy_pass http://java_prod;
include proxy_params;
}
location @java_test {
proxy_pass http://java_test;
include proxy_params;
}
}
//nginx反向代理tomcat,必须配置头部信息否则返回400错误
[root@nginx-lua conf.d]# cat ../proxy_params
proxy_redirect default;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_connect_timeout 30;
proxy_send_timeout 60;
proxy_read_timeout 60;
proxy_buffer_size 32k;
proxy_buffering on;
proxy_buffers 4 128k;
proxy_busy_buffers_size 256k;
proxy_max_temp_file_size 256k;4.编写Nginx调用灰度发布Lua脚本
[root@nginx ~]# cat /etc/nginx/lua/dep.lua
--获取x-real-ip
clientIP = ngx.req.get_headers()["X-Real-IP"]
--如果IP为空-取x_forwarded_for
if clientIP == nil then
clientIP = ngx.req.get_headers()["x_forwarded_for"]
end
--如果IP为空-取remote_addr
if clientIP == nil then
clientIP = ngx.var.remote_addr
end
--定义本地,加载memcached
local memcached = require "resty.memcached"
--实例化对象
local memc, err = memcached:new()
--判断连接是否存在错误
if not memc then
ngx.say("failed to instantiate memc: ", err)
return
end
--建立memcache连接
local ok, err = memc:connect("127.0.0.1", 11211)
--无法连接往前端抛出错误信息
if not ok then
ngx.say("failed to connect: ", err)
return
end
--获取对象中的ip-存在值赋给res
local res, flags, err = memc:get(clientIP)
--
--ngx.say("value key: ",res,clientIP)
if err then
ngx.say("failed to get clientIP ", err)
return
end
--如果值为1则调用local-@java_test
if res == "1" then
ngx.exec("@java_test")
return
end
--否则调用local-@java_prod
ngx.exec("@java_prod")
return5.使用Memcache set IP, 测试灰度发布
//telnet传入值
[root@nginx conf.d]# telnet 127.0.0.1 11211
# set对应IP
set 211.161.160.201 0 0 1
# 输入1
15.Nginx+Lua实现WAF应用防火墙
1.常见的恶意行为
爬虫行为和恶意抓取,资源盗取
防护手段
- 基础防盗链功能不让恶意用户能够轻易的爬取网站对外数据
- ccess_moudle->对后台,部分用户服务的数据提供IP防护
解决方法
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
set $ip 0;
if ($http_x_forward_for ~ 211.161.160.201){
set $ip 1;
}
if ($remote_addr ~ 211.161.160.201){
set $ip 1;
}
# 如果$ip值为0,则返回403, 否则允许访问
location /hello {
if ($ip = "0"){
return 403;
}
default_type application/json;
return 200 '{"status":"success"}';
}2.常见的攻击手段
后台密码撞库,通过猜测密码字典不断对后台系统登陆性尝试,获取后台登陆密码
防护手段
1.后台登陆密码复杂度
2.使用access_module-对后台提供IP防控
3.预警机制
文件上传漏洞,利用上传接口将恶意代码植入到服务器中,再通过url去访问执行代码
执行方式bgx.com/1.jpg/1.php
解决办法
location ^~ /upload {
root /soft/code/upload;
if ($request_filename ~* (.*)\.php){
return 403;
}
}3.常见的攻击手段
利用未过滤/未审核的用户输入进行Sql注入的攻击方法, 让应用运行本不应该运行的SQL代码
防护手段
1.php配置开启安全相关限制
2.开发人员对sql提交进行审核,屏蔽常见的注入手段
3.Nginx+Lua构建WAF应用层防火墙, 防止Sql注入

1.快速安装lnmp架构
[root@nginx ~]# yum install mariadb mariadb-server php php-fpm php-mysql -y2.配置Nginx + php
[root@nginx conf.d]# cat phpserver.conf
server {
server_name 47.104.250.169;
root /soft/code;
index index.html index.php;
location ~ \.php$ {
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /soft/code/$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
}3.配置MySQL
[root@nginx ~]# systemctl start mariadb
MariaDB [(none)]> create database info;
MariaDB [(none)]> use info;
MariaDB [info]> create table user(id int(11),username varchar(64), password varchar(64), email varchar(64));
MariaDB [info]> desc user;
+----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
| username | varchar(64) | YES | | NULL | |
| password | varchar(64) | YES | | NULL | |
| email | varchar(64) | YES | | NULL | |
+----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
//插入数据
MariaDB [info]> insert into user (id,username,password,email) values(1,'bgx',('123'),'bgx@foxmail.com');
MariaDB [info]> select * from info.user;
+------+----------+----------------------------------+-----------------+
| id | username | password | email |
+------+----------+----------------------------------+-----------------+
| 1 | bgx | 123 | bgx@foxmail.com |
+------+----------+----------------------------------+-----------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)5.配置php代码
[root@nginx conf.d]# cat /soft/code/login.html
<html>
<head>
<title> Sql注入演示场景 </title>
<meta http-equiv="content-type"content="text/html;charset=utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<form action="sql.php" method="post">
<table>
<tr>
<td> 用 户: </td>
<td><input type="text" name="username"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> 密 码: </td>
<td><input type="text" name="password"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><input type="submit" value="提交"></td>
<td><input type="reset" value="重置"></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
//被html调用的sql.php文件
[root@nginx conf.d]# cat /soft/code/sql.php
<?php
$conn = mysql_connect("localhost",'root','') or die("数据库连接失败!");
mysql_select_db("info",$conn) or die ("您选择的数据库不存在");
$name=$_POST['username'];
$pwd=$_POST['password'];
$sql="select * from user where username='$name' and password='$pwd'";
echo $sql."<br />";
$query=mysql_query($sql);
$arr=mysql_fetch_array($query);
if($arr){
echo "login success!<br />";
echo $arr[1];
echo $arr[3]."<br /><br />";
}else{
echo "login failed!";
}
?>5.使用lua解决此类安全问题

6.部署Waf相关防护代码
[root@nginx ~]# cd /soft/src/
[root@nginx ~]# git clone https://github.com/loveshell/ngx_lua_waf.git
//把ngx_lua_waf复制到nginx的目录下,解压命名为waf
[root@nginx ~]# cp -r ngx_lua_waf /etc/nginx/waf
//在nginx.conf的http段添加(注意路径)
lua_package_path "/etc/nginx/waf/?.lua";
lua_shared_dict limit 10m;
init_by_lua_file /etc/nginx/waf/init.lua;
access_by_lua_file /etc/nginx/waf/waf.lua;
//配置config.lua里的waf规则目录(一般在waf/wafconf/目录下)
RulePath = "/etc/nginx/waf/wafconf/"
#绝对路径如有变动,需对应修改, 然后重启nginx即可5.Nginx + lua防止Sql注入
[root@nginx ~]# vim /etc/nginx/waf/wafconf/post
\sor\s+
6.防止CC攻击
[root@nginx ~]# vim /etc/nginx/waf/config.lua
CCrate="100/60"