Nginx配置文件
Nginx主配置文件/etc/nginx/nginx.conf是一个纯文本类型的文件,整个配置文件是以区块的形式组织的。一般,每个区块以一对大括号{}来表示开始与结束。
1.Main位于nginx.conf配置文件的最高层
2.Main层下可以有Event、HTTP层
3.HTTP层下面有允许有多个Server层, 用于对不同的网站做不同的配置
4.Server层也允许有多个Location, 用于对不同的路径进行不同模块的配置
nginx默认配置语法
user //设置nginx服务的系统使用用户
worker_processes //工作进程, 配置和CPU个数保持一致
error_log //错误日志, 后面接入的是路径
pid //Nginx服务启动时的pidevents事件模块
events { //事件模块
worker_connections //每个worker进程支持的最大连接数
use //内核模型,select,poll,epoll
}
非虚拟主机的配置或公共配置定义在http{}段内, server{}段外
http {
...
//必须使用虚拟机配置站点, 每个虚拟机使用一个server{}段
'server' {
listen 80; //监听端口, 默认80
server_name localhost; //提供服务的域名或主机名
//控制网站访问路径
'location' / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html; //存放网站路径
index index.html index.htm; //默认访问首页文件
}
//指定错误代码, 统一定义错误页面, 错误代码重定向到新的Locaiton
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
'location' = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
...
//第二个虚拟主机配置
'server' {
...
}
}
Nginx日志配置
在学习日志之前, 我们需要先了解下HTTP请求和返回
curl -v http://www.baidu.com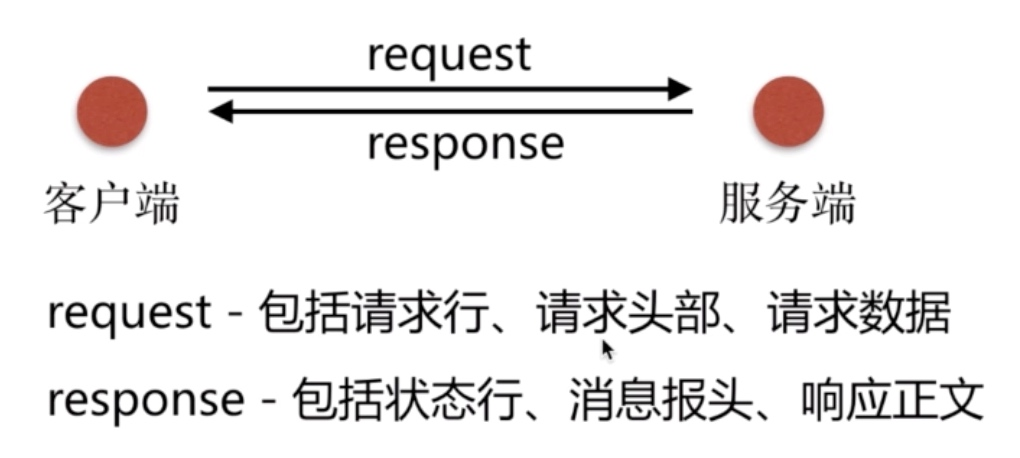
Nginx日志配置规范
配置语法: 包括: error.log access.log
Syntax: log_format name [escape=default|json] string …;
Default: log_format combined “…”;
Context: http
Nginx默认配置
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';Nginx日志变量
$remote_addr //表示客户端地址
$remote_user //http客户端请求nginx认证用户名
$time_local //Nginx的时间
$request //Request请求行, GET等方法、http协议版本
$status //respoence返回状态码
$body_bytes_sent //从服务端响应给客户端body信息大小
$http_referer //http上一级页面, 防盗链、用户行为分析
$http_user_agent //http头部信息, 客户端访问设备
$http_x_forwarded_for //http请求携带的http信息Nginx状态监控
–with-http_stub_status_module 记录Nginx客户端基本访问状态信息
Syntax: stub_status;
Default: —
Context: server, location
具体配置如下:
location /mystatus {
stub_status on;
access_log off;
}Nginx_status概述
Active connections:2 //Nginx当前活跃连接数
server accepts handled requests
16 16 19
server表示Nginx处理接收握手总次数。
accepts表示Nginx处理接收总连接数。
请求丢失数=(握手数-连接数)可以看出,本次状态显示没有丢失请求。
handled requests,表示总共处理了19次请求。
Reading Nginx读取数据
Writing Nginx写的情况
Waiting Nginx开启keep-alive长连接情况下, 既没有读也没有写, 建立连接情况Nginx下载站点
Nginx默认是不允许列出整个目录浏览下载。
Syntax: autoindex on | off;
Default:
autoindex off;
Context: http, server, locationautoindex常用参数
autoindex_exact_size off;
默认为on, 显示出文件的确切大小,单位是bytes。
修改为off,显示出文件的大概大小,单位是kB或者MB或者GB。
autoindex_localtime on;
默认为off,显示的文件时间为GMT时间。
修改为on, 显示的文件时间为文件的服务器时间。
charset utf-8,gbk;
默认中文目录乱码,添加上解决乱码。配置目录浏览功能
开启目录浏览
location / {
root html;
autoindex on;
autoindex_localtime on;
autoindex_exact_size off;
}Nginx访问限制
连接频率限制 limit_conn_module
请求频率限制 limit_req_module
http协议的连接与请求
HTTP是建立在TCP, 在完成HTTP请求需要先建立TCP三次握手(称为TCP连接),在连接的基础上在HTTP请求。
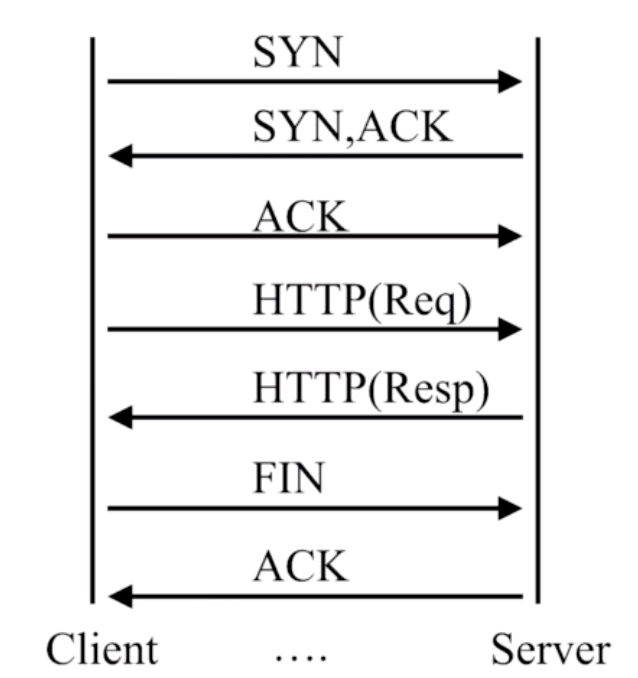
HTTP协议的连接与请求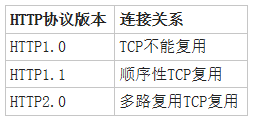
HTTP请求建立在一次TCP连接基础上,一次TCP请求至少产生一次HTTP请求
Nginx连接限制配置
//Nginx连接限制语法
Syntax: limit_conn_zone key zone=name:size;
Default: —
Context: http
Syntax: limit_conn zone number;
Default: —
Context: http, server, location
//具体配置如下:
http {
//http段配置连接限制, 同一时刻只允许一个客户端IP连接
limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=conn_zone:10m;
...
server {
...
location / {
//同一时刻只允许一个客户端IP连接
limit_conn conn_zone 1;
}压力测试
yum install -y httpd-tools
ab -n 50 -c 20 http://127.0.0.1/index.html
Nginx请求限制配置
//Nginx请求限制语法
Syntax: limit_req_zone key zone=name:size rate=rate;
Default: —
Context: http
Syntax: limit_conn zone number [burst=number] [nodelay];
Default: —
Context: http, server, location
//具体配置如下:
http {
//http段配置请求限制, rate限制速率,限制一秒钟最多一个IP请求
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=req_zone:10m rate=1r/s;
...
server {
...
location / {
//1r/s只接收一个请求,其余请求拒绝处理并返回错误码给客户端
limit_req zone=req_zone;
//请求超过1r/s,剩下的将被延迟处理,请求数超过burst定义的数量, 多余的请求返回503
#limit_req zone=req_zone burst=3 nodelay;
}
//压力测试
yum install -y httpd-tools
ab -n 50 -c 20 http://127.0.0.1/index.html连接限制没有请求限制有效?
我们前面说过, 多个请求可以建立在一次的TCP连接之上, 那么我们对请求的精度限制,当然比对一个连接的限制会更加的有效。
因为同一时刻只允许一个连接请求进入。
但是同一时刻多个请求可以通过一个连接进入。
所以请求限制才是比较优的解决方案。
Nginx访问控制
基于IP的访问控制 http_access_module
基于用户登陆认证 http_auth_basic_module
基于IP的访问控制
//允许配置语法
Syntax: allow address | CIDR | unix: | all;
Default: —
Context: http, server, location, limit_except
//拒绝配置语法
Syntax: deny address | CIDR | unix: | all;
Default: —
Context: http, server, location, limit_except
//配置拒绝某一个IP, 其他全部允许
location ~ ^/1.html {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html;
deny 192.168.56.1;
allow all;
}
//只允许某一个网段访问,其它全部拒绝
location / {
root html;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
allow 192.168.56.0/24;
deny all;
}
http_access_module局限性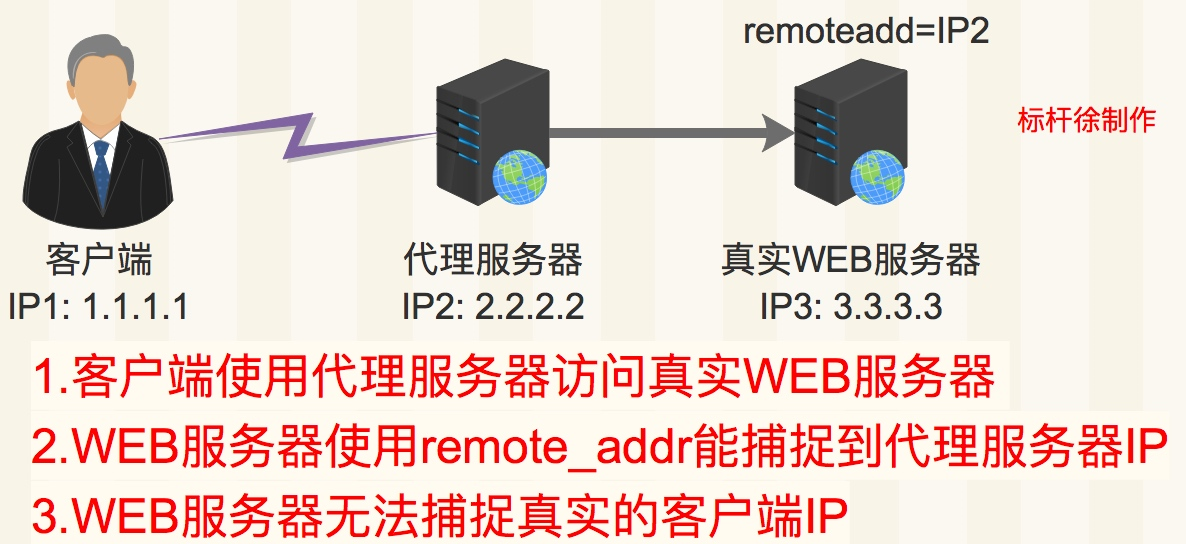
下图是使用http_x_forwarded_for记录真实客户端IP地址以及代理服务器IP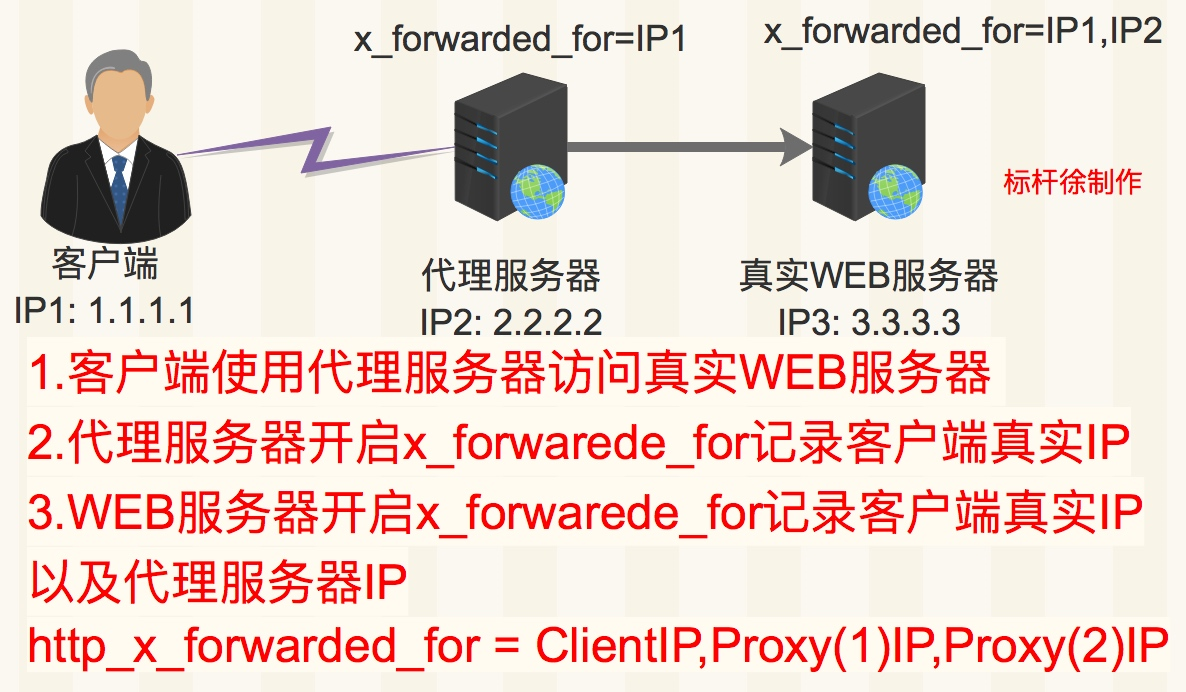
解决方式
1.采用HTTP头信息控制访问, 代理以及web服务开启http_x_forwarded_for
2.结合geo模块作
3.通过HTTP自动以变量传递
基于用户登陆认证
//配置语法
Syntax: auth_basic string| off;
Default: auth_basic off;
Context: http, server, location, limit_except
//用户密码记录配置文件
Syntax: auth_basic_user_file file;
Default: -
Context: http, server, location, limit_except
//需要安装依赖组件
[root@xuliangwei ~]# yum install httpd-tools
[root@xuliangwei ~]# htpasswd -c /etc/nginx/auth_conf xuliangwei
//可在http,server,location下添加如下信息
auth_basic "Auth access Blog Input your Passwd!";
auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/auth_conf;用户认证局限性
1.用户信息依赖文件方式
2.用户管理文件过多, 无法联动
3.操作管理机械,效率低下
解决办法
1.Nginx结合LUA实现高效验证
2.Nginx结合LDAP利用nginx-auth-ldap模块
Nginx虚拟主机
所谓虚拟主机,在web服务器里是一个独立的网站站点,这个站点对应独立的域名(也可能是IP或端口),具有独立的程序及资源目录,可以独立地对外提供服务供用户访问。
配置基于域名虚拟主机
1.创建web站点目录
[root@LNMP conf]# mkdir /soft/code/{www,bbs}
[root@LNMP conf]# echo "www" > /soft/code/www/index.html
[root@LNMP conf]# echo "bbs" > /soft/code/bbs/index.html
2.配置虚拟主机
[root@LNMP conf]# cat conf.d/{www,bbs}.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.xuliangwei.com;
root /soft/code/www;
...
}
server {
...
listen 80;
server_name bbs.xuliangwei.com;
root /soft/code/bbs;
}
配置不同端口访问不同虚拟主机
//仅修改listen监听端口即可, 但不能和系统端口发生冲突
server {
...
listen 8001;
...
}
server {
...
listen 8002;
...
}配置虚拟主机别名
所谓虚拟主机别名,就是虚拟主机设置除了主域名以外的一个域名,实现用户访问的多个域名对应同一个虚拟主机网站的功能。
以www.sunrisenan.com 域名的虚拟主机为例:
为其增加一个别名sunrisenan.com时,出现网站内容和访问www.sunrisenan.com 是一样的,具体配置如下:
//默认配置
[root@LNMP ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.sunrisenan.com;
}
//别名配置
[root@LNMP ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.sunrisenan.com sunrisenan.com;
...
}
//使用Linux下curl测试结果
[root@LNMP conf]# curl sunrisenan.com
www.sunrisenan.com
[root@LNMP conf]# curl www.sunrisenan.com
www.sunrisenan.com//访问带www和不带www是一样的, 除了别名实现也可以通过rewrite实现
域名跳转www
主机记录就是域名前缀,常见用法有:
www:解析后的域名为www.aliyun.com。
@:直接解析主域名 aliyun.com。
*:泛解析,匹配其他所有域名 *.aliyun.com。
mail:将域名解析为mail.aliyun.com,通常用于解析邮箱服务器。
二级域名:如:abc.aliyun.com,填写abc。
手机网站:如:m.aliyun.com,填写m。
显性URL:不支持泛解析(泛解析:将所有子域名解析到同一地址)

法:1:
server {
listen 80;
server_name sunrisenan.com;
rewrite ^(.*) $scheme://www.$server_name$1 permanent;
}法2:
server {
listen *:80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name example.com;
return 301 http://www.example.com$request_uri;
}案例
server {
listen 443;
server_name airknow.com
return 301 https://www.airknow.com$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 default_server ssl;
server_name www.airknow.com;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name airknow.com;
return 301 http://www.airknow.com$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.airknow.com;
return 301 https://www.airknow.com$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443;
server_name www.airknow.com;
ssl on;
#...
} http 跳转https
server {
listen 80;
server_name jump.mcake.com;
#告诉浏览器有效期内只准用 https 访问
add_header Strict-Transport-Security max-age=15768000;
#永久重定向到 https 站点
return 301 https://$server_name$request_uri;
}1,将www.myweb.com/connect 跳转到connect.myweb.com
rewrite ^/connect$ http://connect.myweb.com permanent;
rewrite ^/connect/(.*)$ http://connect.myweb.com/$1 permanent;2,将connect.myweb.com 301跳转到www.myweb.com/connect/
if ($host = "connect.myweb.com"){
rewrite ^/(.*)$ http://www.myweb.com/connect/$1 permanent;
}3,myweb.com 跳转到www.myweb.com
if ($host != 'www.myweb.com' ) {
rewrite ^/(.*)$ http://www.myweb.com/$1 permanent;
}4,www.myweb.com/category/123.html 跳转为 category/?cd=123
rewrite “/category/(.*).html$” /category/?cd=$1 last;
5,www.myweb.com/admin/ 下跳转为www.myweb.com/admin/index.php?s=
if (!-e $request_filename){
rewrite ^/admin/(.*)$ /admin/index.php?s=/$1 last;
}6,在后面添加/index.php?s=
if (!-e $request_filename){
rewrite ^/(.*)$ /index.php?s=/$1 last;
}7,www.myweb.com/xinwen/123.html 等xinwen下面数字+html的链接跳转为404
rewrite ^/xinwen/([0-9]+)\.html$ /404.html last;8,http://www.myweb.com/news/radaier.html 301跳转 http://www.myweb.com/strategy/
rewrite ^/news/radaier.html http://www.myweb.com/strategy/ permanent;9,重定向 链接为404页面
rewrite http://www.myweb.com/123/456.php /404.html last;10, 禁止htaccess
location ~//.ht {
deny all;
}11, 可以禁止/data/下多级目录下.log.txt等请求;
location ~ ^/data {
deny all;
}12, 禁止单个文件
location ~ /www/log/123.log {
deny all;
}13, http://www.myweb.com/news/activies/2014-08-26/123.html 跳转为 http://www.myweb.com/news/activies/123.html
rewrite ^/news/activies/2014\-([0-9]+)\-([0-9]+)/(.*)$ http://www.myweb.com/news/activies/$3 permanent;14,nginx多条件重定向rewrite 如果需要打开带有play的链接就跳转到play,不过/admin/play这个不能跳转
if ($request_filename ~ (.*)/play){ set $payvar '1';}
if ($request_filename ~ (.*)/admin){ set $payvar '0';}
if ($payvar ~ '1'){
rewrite ^/ http://play.myweb.com/ break;
}15,http://www.myweb.com/?gid=6 跳转为http://www.myweb.com/123.html
if ($request_uri ~ "/\?gid\=6"){return http://www.myweb.com/123.html;}正则表达式匹配,其中:
~ 为区分大小写匹配
~* 为不区分大小写匹配
!
和!*分别为区分大小写不匹配及不区分大小写不匹配
文件及目录匹配,其中:
-f和!-f用来判断是否存在文件
-d和!-d用来判断是否存在目录
-e和!-e用来判断是否存在文件或目录
-x和!-x用来判断文件是否可执行
flag标记有:
last 相当于Apache里的[L]标记,表示完成rewrite
break 终止匹配, 不再匹配后面的规则
redirect 返回302临时重定向 地址栏会显示跳转后的地址
permanent 返回301永久重定向 地址栏会显示跳转后的地址
Nginx慢请求日志记录
